Supporting growth while guaranteeing performance
The advent of 5G is an exciting time for service providers. Those that can converge and optimize their networks will be able to offer diverse new services that deliver a competitive advantage and contribute to top line growth. In fact, in ‘The guide to capturing the 5G industry digitalization business potential’, Ericsson delves deeper into how operators can potentially grow revenues up to 36 percent by addressing 10 key industry sectors.
While much of the excitement is focused on the mobile element of 5G, the fact is that delivering successful 5G services will place new challenges on the entire transport network, from the cell site to the core.
So, what are these challenges? Ericsson and Juniper Networks jointly refer to them as the 5 Challenges of 5G, all of which need to be addressed to support growth and guarantee superior 5G performance.
5G CHALLENGES
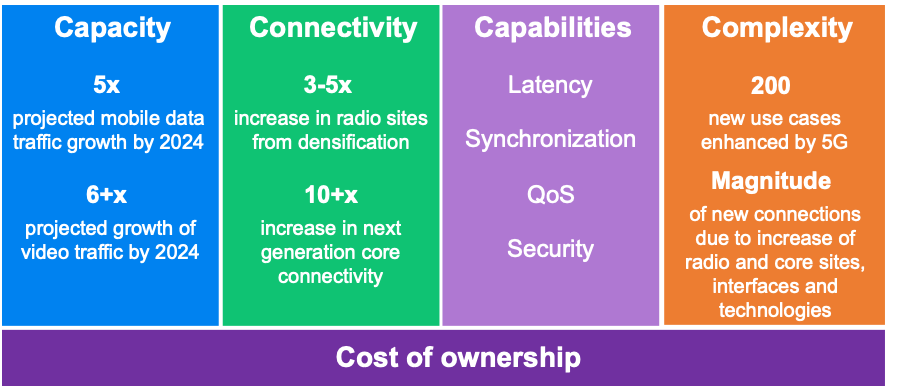
Source: Ericsson
Increased Capacity and Connectivity
With hundreds of potential new use cases and the spectacular growth of the Internet of Things (IoT), 5G networks must be able to handle massive increases in capacity and connectivity. From 2018 to 2024, total mobile data traffic is expected to increase by a factor of five according to the Ericsson Mobility Report November 2018 edition and, in the same time frame, video traffic will increase over 6 times.
>With the use of middle-and-high-spectrum frequencies, more base stations will be necessary due to the shorter distances that traffic can be transmitted over. Because of the many new locations to manage, service providers will also face new environmental considerations, new types of access points and new interface types. This densification, of which a significant amount will come from small cells, is expected to increase the connectivity in the network by 3 to 5 times.
Enhanced Capabilities
New services and applications such as autonomous cars, remote healthcare and virtual reality are expected to create the need for new network capabilities. As we discussed in a previous blog, these applications are expected to require extremely low latency, which can only be delivered by having compute power at the edge.
Meeting timing and synchronization requirements in 5G is a key requirement that is gaining increasing attention among operators. While network-based timing and synchronization are standard procedure for mobile networks in many parts of the world, North America, to date, relies mainly on GPS clocks. However, GPS in dense, urban areas populated by small cells (many indoors) may not be viable economically, or in many cases, technically, due to interference. Additionally, in the case of losing a GPS-based clock source, it is hard to hold the required synchronization accuracy for more than one hour. To meet reliability demands, there is an emerging need for backup timing via the network, even when GPS is present.
Quality of service (QoS) will need to improve, too. Network slicing is expected to add additional QoS granularity and will enable service providers to prioritize network packets more effectively, gain greater control of traffic flow and support new and enhanced 5G use cases across the same physical network.
Finally, as we have discussed before (Blog: The Role of Edge Cloud in Securing the Internet of Things), the new network, increased antennas and the proliferation of IoT will bring new security challenges that can only be addressed with end-to-end, device-to-core security solutions.
Increased Complexity and Low Cost of Ownership
The new capabilities combined with the sheer magnitude of new connections driven by the increase in radio and core sites, interfaces and technologies will lead to greater complexity in the network. Coping with this complexity will require high levels of automation, seamless management and control, and effective cross-domain orchestration between the radio, core and transport elements of the network.
New Operating Model
Market expectations of 5G are high. Personal users – and commercial and public sector organizations — expect to connect seamlessly to the new network and benefit from new connectivity, services and applications. But the fact is they don’t expect to pay more. Therefore, service providers must also find a way to manage costs. Doing so will require greater radio efficiencies, as well as increased automation, higher productivity and more cost effectiveness built into every element of their investment.
Working together, Ericsson and Juniper have developed an integrated end-to-end solution, from radio to core, that addresses the five challenges in 5G. It enables service providers to create a highly orchestrated, secure and cost-effective end-to-end solution for delivering high quality 5G services to our customers. Discover how your organization can benefit from our joint solution.